For Windows OS who want to try Linux without completely removing Windows OS, dual booting Linux along with Windows OS is the best way to experience the best of Linus OS and Windows OS. Dual Booting Linux on Windows OS will let a user choose the OS to use when booting. After trying out Linux OS, if a user wants to remove the Linux OS, it is also easy to do so. In this post, how to remove Linux installation from dual boot with Windows OS.
There are many flavors of Linux OS we can try. Ubuntu is one of the most popular Linux distributions. Whatever the distro, during the installation of Linux OS with dual boot, we allocate separate partition / space on the hard disk for the Linux OS to reside in. When we login to Windows OS, the space used by Linux is also visible in the Device Manager > Disk Management as a separate partition.
To remove Linux OS from Dual Boot with Window OS (Deleting Linux partition in Windows ), follow the steps below:
- Log in to Windows.
- Press Windows+R and run diskmgmt.msc command to open Windows disk management tool.
OR
Right click on “This PC / My Computer” > Manage > Storage > Disk Management - Check the disk partitions
- Identify the partition used by Linux OS.
- It would be easy to identify by its disk size.
- Another way to identify Linux partition is look for file system and drive letters on the partitions. Windows partition are labeled with a drive letters such as C, D, E etc and file system will usually be NTFS or FAT file system.
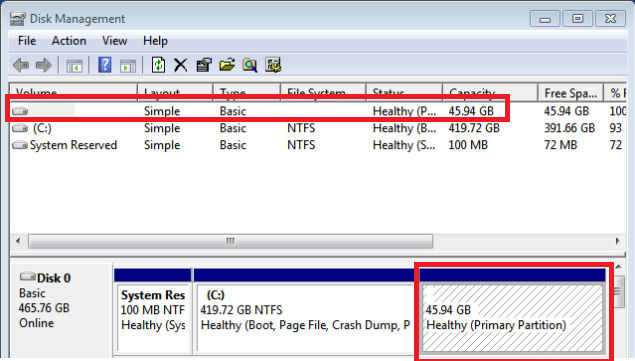
- Right-click on the Linux partition and choose “Delete Volume.”
This will delete the partition from your hard drive and leave free space. If the partition still shows “green” meaning “free space,” right-click on it again and choose “Delete Volume”. The partition should now show “black” – “Unallocated Space.” - To let Windows partition occupy the unallocated space, Right-click on the Windows partition left of the Unallocated space created from the previous Linux partition and choose “Extend Volume.”
The Windows partition will then take over the left over unallocated space. - Fix the Windows MBR
- Put the Windows installation disk /Windows recovery disc (or recovery USB drive) and restart the computer.
- Press F10 or F12 at the boot time to go into BIOS/UEFI and choose to boot from removable disk / USB
- Choose to repair the computer
- Go for “Troubleshoot” option
- In troubleshoot page, choose for Advanced options
- Look for command prompt option and click
- In the command line, type the following command to fix the Windows boot loader:
bootrec.exe /fixmbr
- Restart the computer
- Windows should boot normally from hard disk.
The Linux OS is successfully removed leaving Windows OS as it is.
Related:
Installing Linux OS by completely removeing Windows OS
Installation of latest Ubuntu 16.04 from USB stick replacing Windows
Installation of Linux OS (Ubuntu) on virtual machine without dual boot.
How To Install Ubuntu On Windows Using Oracle Virtual Box (run Ubuntu on Windows) ?




